The odds ratio supports clinical decisions by providing information on the odds of a particular outcome relative to the odds of another outcome In the endocarditis example, the risk (or odds) of dying if treated with the new drug is relative to the risk (odds) of dying if treated with the standard treatment antibiotic protocol If we go a step further, we can calculate the ratio between the two risks, called relative risk or risk ratio (RR), which indicates how much more likely is the occurrence of the event in one group compared with the other group Meanwhile, the odds represents a quite different conceptAbout Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us Creators

Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated
Odds ratio vs relative risk confidence interval
Odds ratio vs relative risk confidence interval- Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeable Relative measures of effect are risk ratio (ie the ratio between two incidence proportions), incidence rate ratio (the ratio between two incidence rates), and OR (the ratio between two odds) The risk difference is an absolute measure of effect (ie the risk of the outcome in exposed individuals minus the risk of the same outcome in unexposed)




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To
Risk Ratio For the study examining wound infections after incidental appendectomy, the risk of wound infection in each exposure group is estimated from the cumulative incidence The relative risk (or risk ratio) is an intuitive way to compare the risks for the two groupsEven an odds ratio; An Odds Ratio (OR) then is simply the comparison of two odds, OR=Odds (A)/Odds (B) The Relative Risk (RR) is simply the comparison of two risks or probabilities, RR=Probability (A)/Probability (B) This is made more clear when the term is referred to as the Risk Ratio Let's look at this graphically
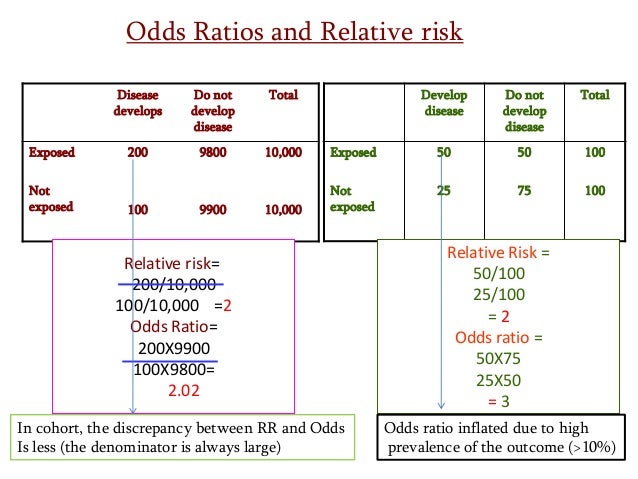
RR Relative risk or RR is very common in the literature, but may represent a risk ratio, ;Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either of
The simple relative risk is 055 and the simple odds ratio is 025Clearly the probability of fathering a child is strongly dependent on a variety of demographic variables, especially age (the issue of marital status was dealt with by a separate analysis) The control group was 84 years older on average (435 years versus 351), showing the need to adjust for this variableSometimes, we see the log odds ratio instead of the odds ratio The log OR comparing women to men is log(144) = 036 The log OR comparing men to women is log(069) = 036 log OR > 0 increased risk log OR = 0 no difference in risk log OR < 0 decreased risk Odds Ratio 0 5 10 15 More on the Odds Ratio Log Odds Ratio4 2 0 2 4 risk = odds/(1odds) "Most published research providing an odds ratio as a measure of effect size should also provide sufficient information for the baseline risk, and hence the relative risk, to be calculated If numbers in each group are given, the crude relative risk can be calculated directly" – BMJ 14;348f7450 doi /bmjf7450



Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram




A Beginner S Guide To Interpreting Odds Ratios Confidence Intervals And P Values Students 4 Best Evidence
In the general medical literature, rate is often incorrectly used for prevalence measuresA prevalence ratio, or ; RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO Risk and Odds just seemed the same to me for a long time Since then, I have come to understand to important difference Lets start with Relative Risk Relative Risk can be addressed by asking the following question How many times more likely is an "exposed" group to develop a



Silo Tips Download Transcript Measuring Risk In Epidemiology B D A C Measuring Risk In Epidemiology




Case Control Study Wikipedia
RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO An RR (or OR) more than 10 indicates an increase in risk (or odds) among the exposed compared to the unexposed, whereas a RR (or OR)Odds ratio versus relative risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good and the odds ratio can be used The ratio of these is the risk ratio, a relative measure of association Risk Ratio = CI e /CI u = 090/058 = 155 Interpretation Smokers had 155 times the risk of respiratory disease compared to nonsmokers over an 18 year period of observation Using the same cumulative incidences we can calculate the risk difference, an absolute measure




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk
Odds Ratio versus Relative Risk Since it is a ratio of ratios, the odds ratio is very difficult to interpret The relative risk is easier to interpret, so the odds ratio alone is not very helpful However, there are certain commonly occurring situations in which the estimate of the relative risk is not very good, and the odds ratio can be usedThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a ) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions Neither the risk ratio nor the odds ratio can be calculated for a studyRelative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test I) Relative Risk A) Simply, relative risk is the ratio of p 1/p 2 For instance, suppose we wanted to take another look at our Seat belt safety data from Florida Safety equipment Injury in use Fatal Nonfatal Total None 1,601 165,527 167,128 Seat belt 510 412,368 412,878




Common Measures Of Association In Medical Research Handout



Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
For estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithm We can specify this manually, or just use a builtin family for our generalized linear model for which the logarithm is the canonical link fucntion, and hence the defaultDifferenz zwischen Odds Ratio und Relatives Risiko Differenz zwischen 21 Odds Ratio vs Relatives Risiko Das relative Risiko (RR) ist einfach die Wahrscheinlichkeit oder Beziehung zweier Ereignisse Nehmen wir an, A ist Ereignis 1 und B ist Ereignis 2 Man kann das RR erhalten, indem man B von A oder A / B dividiert A crude odds ratio can be converted to a crude risk ratio risk ratio = odds ratio/(1 − p0) (p0 × odds ratio), in which p0 is the outcome prevalence (risk) among the unexposed Some have applied this formula to an adjusted odds ratio to obtain an adjusted risk ratio 49 This method can produce biased risk ratios and incorrect confidence




Odds Ratio Relative Risk



Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data
Odds Ratio, Hazard Ratio and Relative Risk Janez Stare1 Delphine MaucortBoulch2 Abstract Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why that would be true But since such perception is mostly Odds ratio is a very effective way of determining association between two variables, mostly influence of one factor on the outcome of interest If strong enough, and the statistical analysis robust enough, it can even determine causality ie prove a cause – effect relationship between a risk factor and disease or an adverse effect and Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




The Difference Between Relative Risk And Odds Ratios The Analysis Factor
Risk ratios, odds ratios, and hazard ratios are three ubiquitous statistical measures in clinical research, yet are often misused or misunderstood in their interpretation of a study's results A 01 paper looking at the use of odds ratios in obstetrics and gynecology research reported 26% of studies (N = 151) misinterpreted odds ratios as risk ratios , while a For example, a relative risk of 15 would suggest a 50% increase in risk, whereas a relative risk of 05 would suggest a 50% decrease in risk Odds ratios The main difference between this and the other two measures is that there is no way of including a Odds ratio (OR) and risk ratio (RR) are two commonly used measures of association reported in research studies In crosssectional studies, the odds ratio is also referred to as the prevalence odds ratio (POR) when prevalent cases are included, and, instead of the RR, the prevalence ratio (PR) is calculated



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean
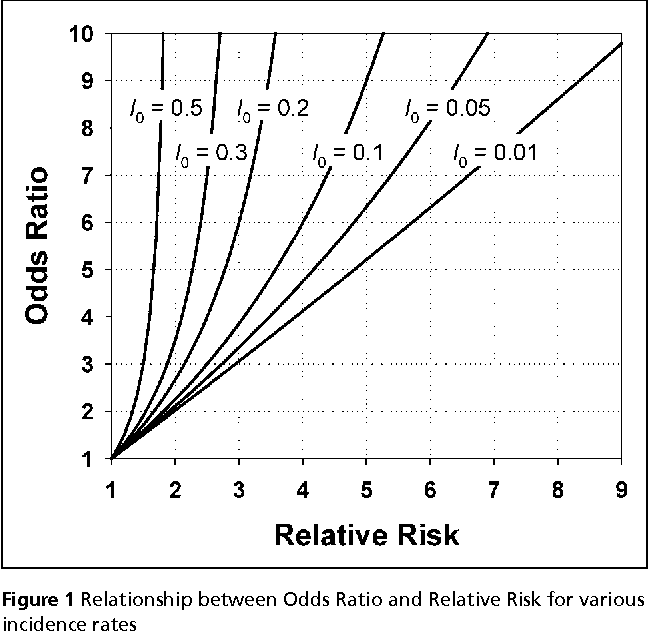
For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean);When the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative riskThe absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group




Relation Between The Odds Ratio Relative Risk And Baseline Risk



Q Tbn And9gcsdciarve4qxmues2ip Qg8ugk1mshcabjsxsnb3oitlp1asplq Usqp Cau
Example Data Odds ratio versus relative risk A hypothetical data set was created to illustrate two methods of estimating relative risks using Stata The outcome generated is called lenses, to indicate if the hypothetical study participants require corrective lenses byThe odds ratio can also be used to determine whether a particular exposure is a risk factor for a particular outcome, and to compare the magnitude of various risk factors for that outcome OR=1 Exposure does not affect odds of outcome OR>1 Exposure associated with higher odds of outcome OR Relative risks versus odds ratios Researchers investigated the effectiveness of a probiotic drink containing Lactobacillus for the prevention of any diarrhoea associated with antibiotic use in hospital A randomised double blind placebo controlled trial study design was used



6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 Review Incidence And Prevalence Are Formally Defined On Slide 7 Birth And Death Rates Are Also Estimates Of Absolute Risk Risk Factors Are Identified By Determining




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology
There can be substantial difference in the association of a risk factor with prevalent disease versus ; Odds ratio vs relative risk Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect sizeOdds ratio and relative risk




Figure 2 X 2 Table With Statpearls Ncbi Bookshelf



Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf
When the RR is exactly 1, the risk is unchanged For example, a report may state 'The relative risk of blindness in people given drug T was 15' This shows that the drug increased the risk of blindness Another measure that is used is the odds ratio For practical purposes, assume that the odds ratio is the same as the relative riskRelative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter to expected results, putting the onus on the researcher to justify them Similarly, you should find If the relative risk is 1, the tutoring made no difference at all If it's above 1, then the tutored group actually had a higher risk of failing than the controls Odds Ratio The odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event in the Treatment group to the odds




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 Ppt Video Online Download




Chapter 6 Choosing Effect Measures And Computing Estimates Of Effect Cochrane Training
Odds is the number having the outcome divided by the number not having the outcome The risk or odds ratio is the risk or odds in the exposed group divided by the risk or odds in the control group A risk or odds ratio = 1 indicates no difference between the groups A risk ratio of 10 indicates identical risk among the two groups A risk ratio greater than 10 indicates an increased risk for the group in the numerator, usually the exposed group A risk ratio less than 10 indicates a decreased risk for the exposed group, indicating that perhaps exposure actually protects against disease occurrenceThe relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population



Confidence Interval For Relative Risk Ppt Video Online Download




Risk And Numbers Needed To Treat Litfl Ccc
A rate ratio, ;Pute either the odds ratio or the relative risk to answer this question The odds ratio compares the relative odds of death in each group For women, the odds were exactly 2 to 1 against dying (154/308 05) For men, the odds were almost 5 to 1 in favor of death (709/142 4993) The odds ratio is 9986 (4993/05) There is a 10fold greaterThe relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative risk



Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios
Relative risk, Risk difference and Odds ratio When the data to be analyzed consist of counts in a crossclassification of two groups (or conditions) and two outcomes, the data can be represented in a fourfold table as follows Several statistics can be calculated such as relative risk and risk difference, relevant in prospective studies, andOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)



Interpretation Of Odds Ratio And Fisher S Exact Test By Sergen Cansiz Towards Data Science



Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Usmle The Journey



Estimating Risk
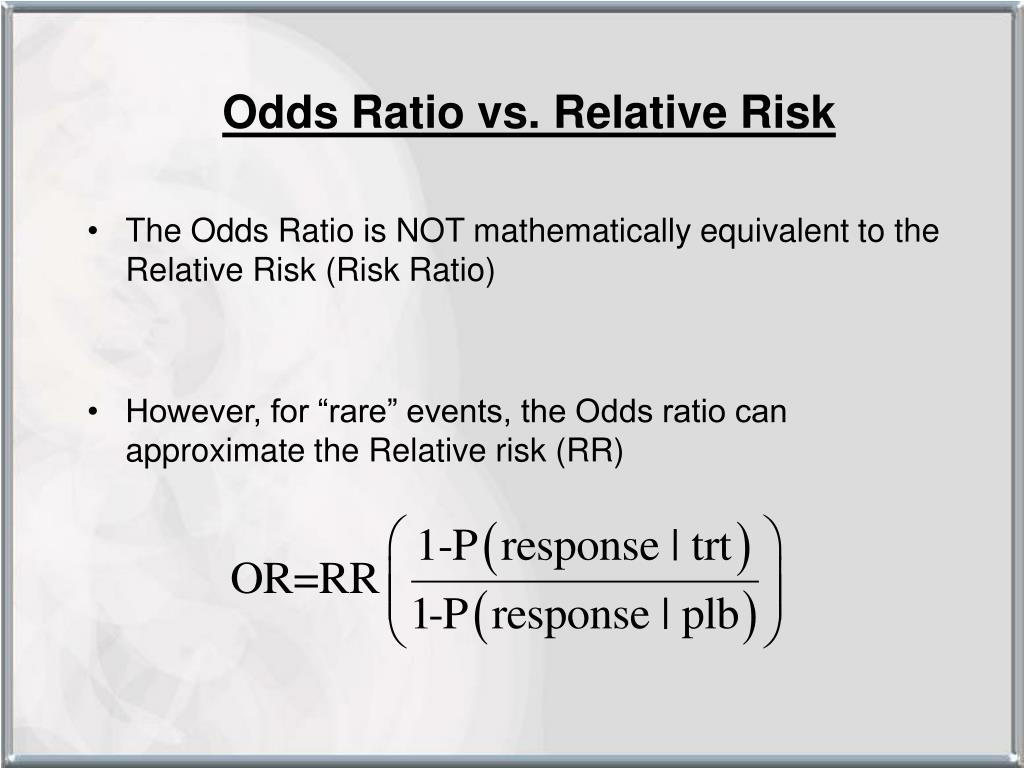



Ppt Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08 Powerpoint Presentation Id




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough




Hsrp 734 Advanced Statistical Methods June 5 08




Relative Risk And Absolute Risk Definition And Examples Statistics How To



Analytical Studies




Risk Differences And Rate Differences




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Relative Risks And Odds Ratios What S The Difference Mdedge Family Medicine




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Relative Risk Ratios And Odds Ratios




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj



Introduction To Genetic Epidemiology Lesson 5 Analyzing The Data




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk




Categorical Data Ziad Taib Biostatistics Astra Zeneca February




Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals



1




Literature Search



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Research Statistics Basics Contents 1 Basic Concepts 2 References Basic Concepts Null Hypothesis The Hypothesis That The Independent Variable Has No Effect On The Dependent Variable For Example Steroids Do Not Improve Outcomes In Ards Would Be



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




Kevin Whelan If You Re Struggling With Odds Ratios Relative Risks Standardised Mean Differences And Number Needed To Treat And The Associated Alphabet Soup Or Rr Smd Nnt Then This Paper




Glossary Of Research Terminology




1 The Odds Ratio Relative Odds In A Case Control Study We Do Not Know The Incidence In The Exposed Population Or The Incidence In The Nonexposed Population Ppt Download




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy In Population Perspective Made Easy On Vimeo




Relative Risk Wikipedia



7 6 Vaccine Effectiveness Management Of A Measles Epidemic




Relative Risk Reduction Can Be Relatively Misleading Youtube




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Difference And Number Needed To Treat Sciencedirect



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia



Relative Risk Ratio Vs Odd Ratio Ppt Authorstream




1 Relative Risks Odds Ratios Or Hazard Ratios Of Risk Factors For Download Table



Confluence Mobile Wiki Ucsf




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk Semantic Scholar




Calculation Of Relative Risks Rr And Odd Ratios Or Download Table




Quiz 5 Flashcards Quizlet




Measures Of Disease Association Measuring Occurrence Of New Outcome Events Can Be An Aim By Itself But Usually We Want To Look At The Relationship Between Ppt Download




Odds Ratio Article



Q Tbn And9gctxz8owky Sul84xtk4ggzacxwhkmhguhlxwyjj9avufagdrhwm Usqp Cau




What Is The Difference Between The Risk Ratio Rr And The Odds Ratio Or Quora




Estimating Risk
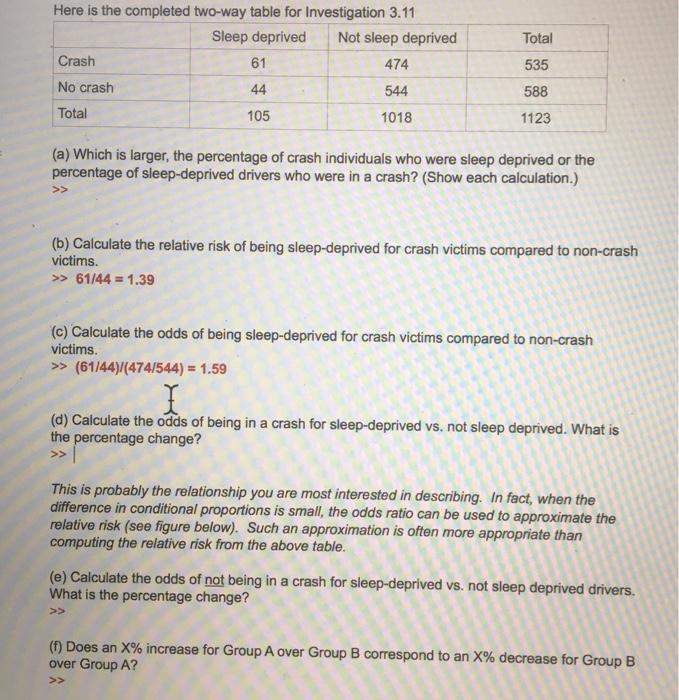



Using Relative Risk And Odds Ratio I Am Confused Chegg Com




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube




Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
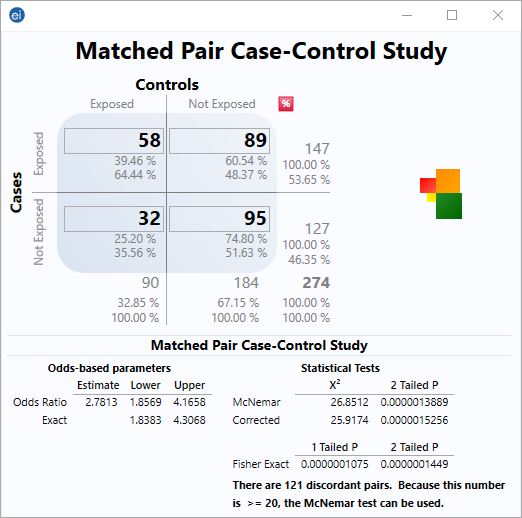



Matched Pair Case Control Statcalc User Guide Support Epi Info Cdc




Measures Of Association Stats Medbullets Step 1




Math3010 Week 6



Med Mahidol Ac Th Ceb Sites Default Files Public Pdf Academic 16 Race611 Ebm Risk study 16 Vallibhakara sa 10 12 16 Print Pdf



Epidemiology Stepwards



Relative Risk Wikipedia




Math Formula To Reproduce A Plot Comparing Relative Risk To Odds Ratios Cross Validated




Numerators Denominators And Populations At Risk Health Knowledge




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




How To Be Awesome At Biostatistics And Literature Evaluation Part Ii Tl Dr Pharmacy




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1
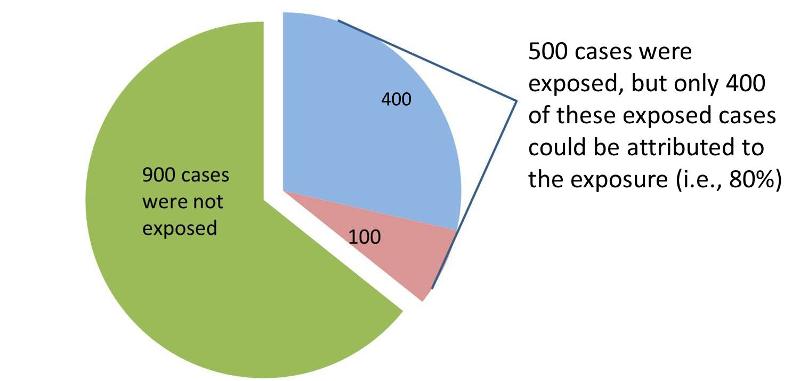



Measures Of Association




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1




Definition And Calculation Of Odds Ratio Relative Risk Stomp On Step1



Icare An R Package To Build Validate And Apply Absolute Risk Models




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Odds Ratio Relative Risk



Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Authorstream




Present Example Of An Dolds Ratio Compared To A Chegg Com




33 Epidemiology Ideas Cohort Study Case Control Study Study Design




On Biostatistics And Clinical Trials Odds Ratio And Relative Risk




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube
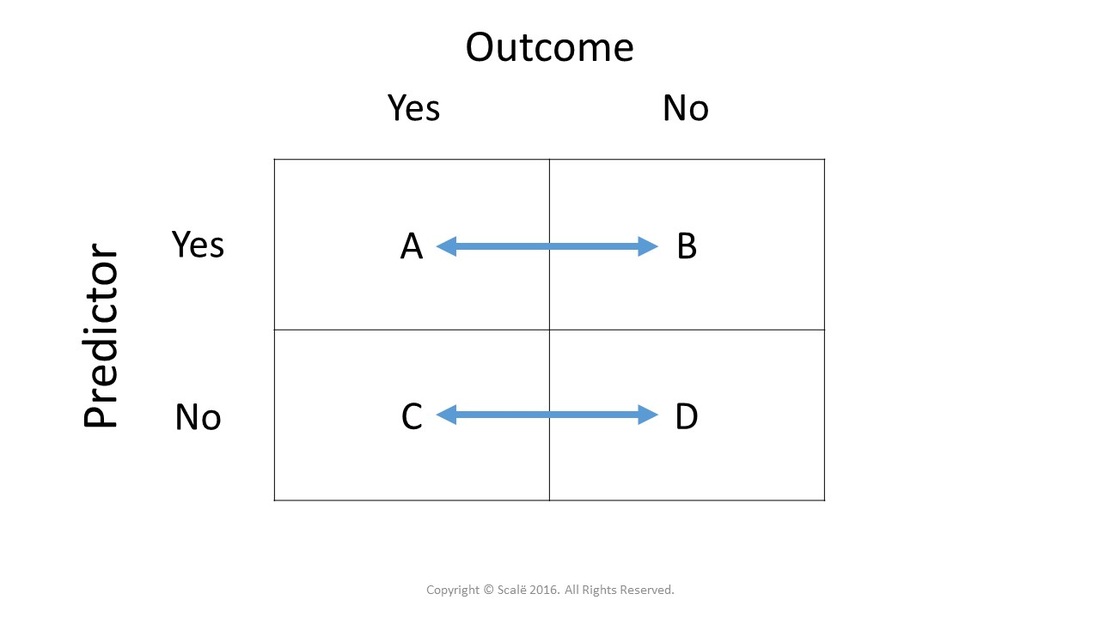



Calculate Relative Risk With 95 Confidence Intervals




Useful Concept For Medical Healthcare Data Risk Prediction




Odds Ratio Relative Risk By Susi Delaney




Odds Ratios Versus Relative Risk




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿